Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, where data is the lifeblood of businesses and organizations, cybersecurity has emerged as a critical discipline. As cyber threats continue to evolve in sophistication and complexity, organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in their cybersecurity endeavors. Understanding the most common cybersecurity threats in 2023 is essential for devising effective defense strategies and safeguarding valuable information.
1. Phishing Attacks: The Art of Deception

Phishing attacks remain one of the most prevalent and effective cyber threats, leveraging deceptive emails or messages to trick users into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links. These attacks often masquerade as legitimate communications from trusted sources, such as banks, social media platforms, or government agencies.
2. Malware: Unwanted Guests in Your Digital Space

Malware encompasses a wide range of malicious software designed to harm computers and systems. It includes viruses, worms, Trojan horses, and ransomware, each with its own unique modus operandi. Malware can steal data, disrupt operations, and even hold systems hostage for ransom.
3. Ransomware: The Encryptor of Valuables
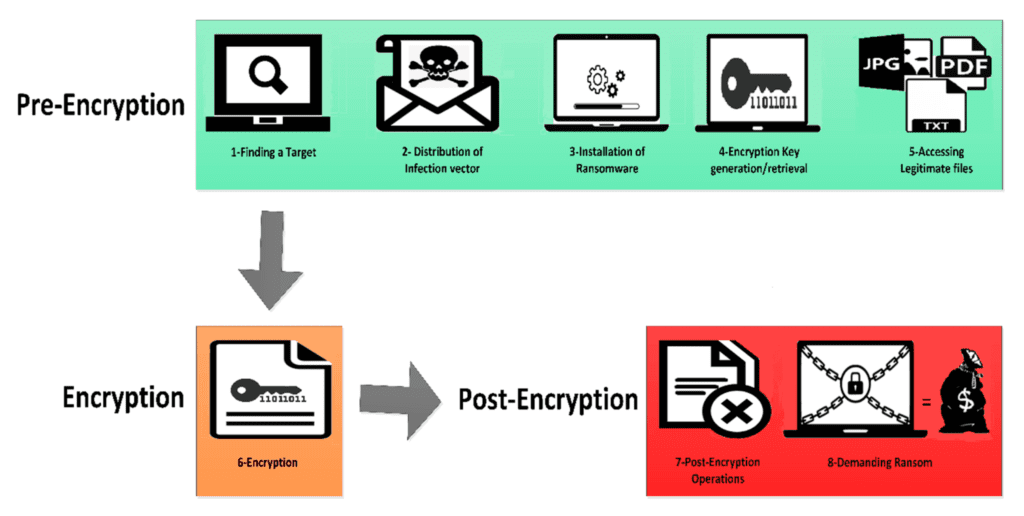
Ransomware has gained notoriety in recent years, wreaking havoc on organizations and individuals alike. This type of malware encrypts critical files, rendering them inaccessible until a ransom payment is made to the attackers. Ransomware attacks can cause significant financial losses and operational downtime.
4. Social Engineering: Exploiting Human Vulnerabilities

Social engineering attacks rely on psychological manipulation and trickery to exploit human vulnerabilities and gain access to sensitive information or systems. Attackers may impersonate trusted individuals, leverage social media platforms, or create false narratives to deceive their targets.
5. Supply Chain Attacks: Targeting the Weakest Link

Supply chain attacks target third-party vendors or partners to gain access to an organization’s network or data. Attackers may compromise software updates, infiltrate vendor systems, or exploit vulnerabilities in third-party services to breach the target organization.
6. Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: The Unknown Threat

Zero-day vulnerabilities are software flaws that are unknown to the software vendor and have not yet been patched. These vulnerabilities pose a significant risk as attackers can exploit them before a patch is available, leaving organizations exposed.
7. Cloud Security: Protecting Data in the Digital Sky

Cloud computing has become an integral part of modern business operations, but it also introduces new security challenges. Cloud security concerns safeguarding data and systems stored in cloud environments, ensuring compliance with cloud security standards, and mitigating cloud-specific risks.
8. Internet of Things (IoT) Security: Securing the Connected World

The growing proliferation of IoT devices has expanded the attack surface, creating new vulnerabilities. IoT security focuses on protecting these devices from cyberattacks, ensuring data privacy, and managing the security risks associated with connected devices.
9. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Security

AI and ML are transforming various industries, but they also introduce new security considerations. AI security focuses on protecting AI models and algorithms from manipulation or attacks, while ML security addresses vulnerabilities in ML systems.
10. Mobile Security: Protecting Data on the Go

Mobile devices have become an essential part of our lives, but they also carry security risks. Mobile security focuses on protecting mobile devices from malware, unauthorized access, and phishing attacks, ensuring data privacy and compliance with mobile security policies.
Conclusion
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, and organizations must remain vigilant and proactive to combat the ever-increasing threats. Understanding the most common cybersecurity threats in 2023 is the first step towards devising effective defense strategies. By implementing robust security measures, educating employees about cybersecurity risks, and collaborating with cybersecurity experts, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of cyberattacks and safeguard their valuable assets in the digital age.